

NASA's Parker Solar Probe sets new distance and speed records during its 10th flyby of the sun, coming.Sponsored Is Manscaped REALLY that good? We spoke to five guys who have been using the grooming products and they.Explosion in ocean life 2 billion years ago helped create Earth's mountains: Large amounts of plankton.
 Hanukkah sling stone that was used against Jewish rebels more than 2,000 years ago bears the name of a Greek.
Hanukkah sling stone that was used against Jewish rebels more than 2,000 years ago bears the name of a Greek. 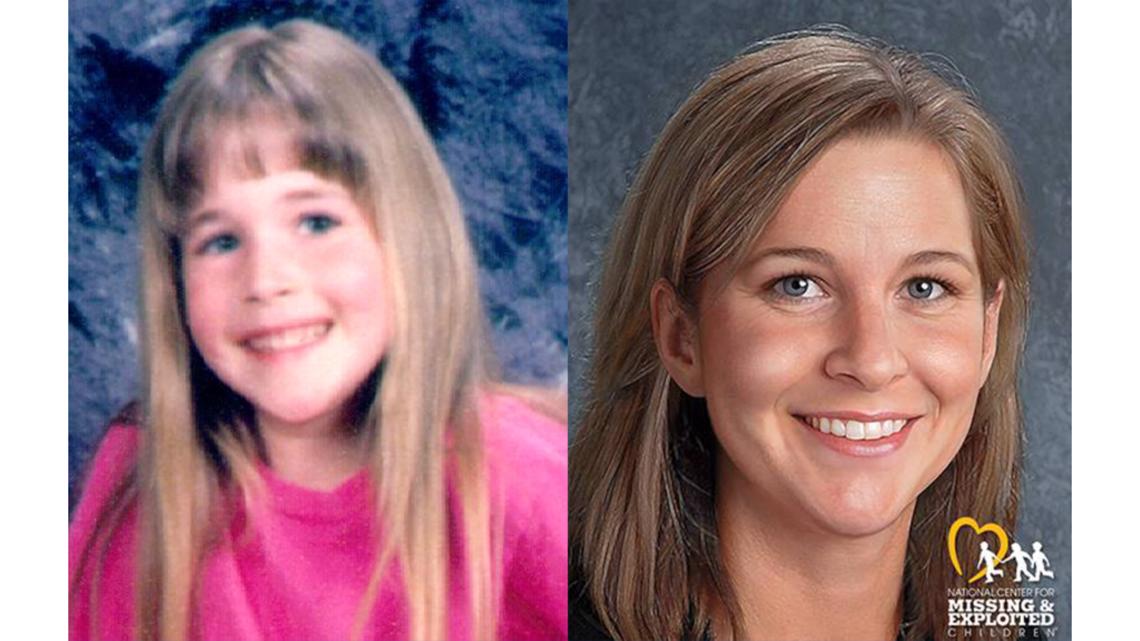 Strength of COVID-19 antibodies depends on age and sex: Study finds levels are higher for women and children. The first 'living robots' that can REPRODUCE: Microscopic organisms made from frog cells assemble 'babies'. Mysterious mummy dating back up to 1,200 years is discovered in an underground tomb in Peru with its whole. ‘When shown images of an age-progressed child photo and a photo of the same person as an adult, people are unable to reliably identify which one is the real photo.’ ‘Our extensive user studies demonstrated age progression results that are so convincing that people can't distinguish them from reality,’ said co-author Steven Seitz, Professor of Computer Science and Engineering. In an experiment asking random users to identify the correct aged photo for each example, they found that users picked the automatically rendered photos about as often as the real-life ones. This technique leverages the average of thousands of faces of the same age and gender, then calculates the visual changes between groups as they age to apply those changes to a new person's face. The shape and appearance of a baby's face – and variety of expressions – often change drastically by adulthood, making it hard to model and predict that change. People could not distinguish between the real and rendered images. The researchers tested their rendered images against those of 82 actual people photographed over a span of years. These changes are then applied to a new child's photo to predict how she or he will appear for any subsequent age up to 80.
Strength of COVID-19 antibodies depends on age and sex: Study finds levels are higher for women and children. The first 'living robots' that can REPRODUCE: Microscopic organisms made from frog cells assemble 'babies'. Mysterious mummy dating back up to 1,200 years is discovered in an underground tomb in Peru with its whole. ‘When shown images of an age-progressed child photo and a photo of the same person as an adult, people are unable to reliably identify which one is the real photo.’ ‘Our extensive user studies demonstrated age progression results that are so convincing that people can't distinguish them from reality,’ said co-author Steven Seitz, Professor of Computer Science and Engineering. In an experiment asking random users to identify the correct aged photo for each example, they found that users picked the automatically rendered photos about as often as the real-life ones. This technique leverages the average of thousands of faces of the same age and gender, then calculates the visual changes between groups as they age to apply those changes to a new person's face. The shape and appearance of a baby's face – and variety of expressions – often change drastically by adulthood, making it hard to model and predict that change. People could not distinguish between the real and rendered images. The researchers tested their rendered images against those of 82 actual people photographed over a span of years. These changes are then applied to a new child's photo to predict how she or he will appear for any subsequent age up to 80. KASPAROV CHESS FOR MOBILE FREE DOWNLOAD SOFTWARE
The software determines the average pixel arrangement from thousands of random Internet photos of faces in different age and gender brackets.Īn algorithm then finds correspondences between the averages from each bracket and calculates the average change in facial shape and appearance between ages.




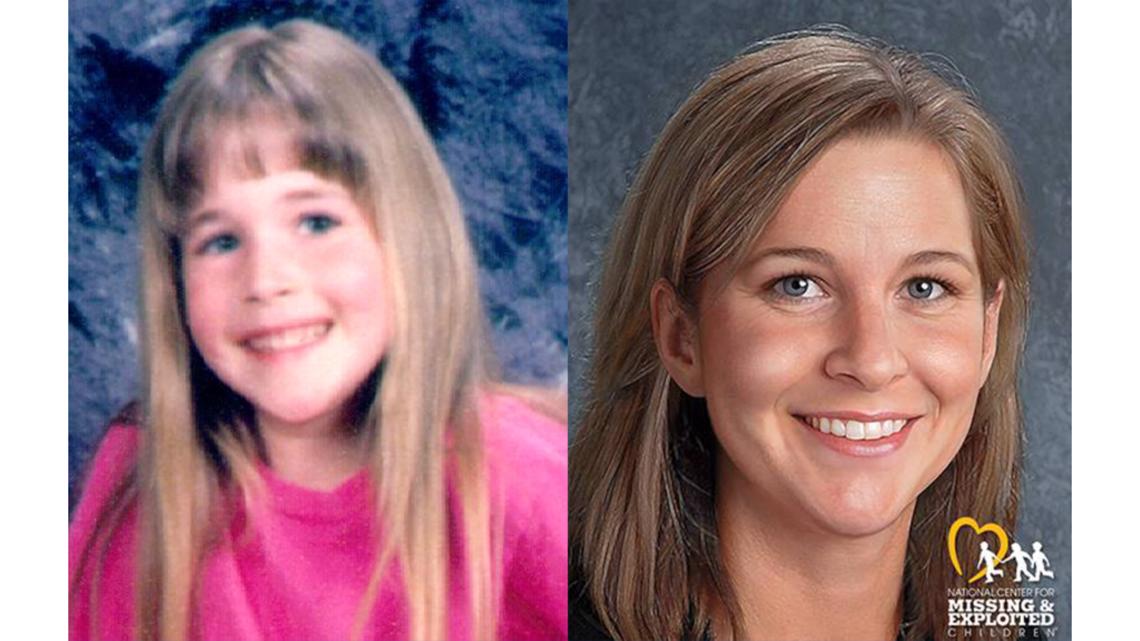


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
